Many of the components of the PDS system are packaged as Java-based web applications and require a Java Application Server to host them. Although there are a few free choices out on the market (e.g., Glassfish, Jetty, etc.) the EN development team consistently uses Apache Tomcat as its application server of choice. This document details the download, installation and configuration of an Apache Tomcat server for use in hosting PDS web applications.
New releases of the Apache Tomcat server are made available periodically, with the latest version of 7.0.X available from the Apache Tomcat 7 Downloads page. Version 8.5.X is available from the Apache Tomcat 8 Downloads page. The download page has several binary distributions to choose from:
The first two listed under the Core bullet work nicely in UNIX-based environments. This deployment example assumes download and installation of the TAR/GZIP package. Select the link of the desired package to download the file to a local machine. In UNIX-based environments it is common to install additional machine-wide accessible software in the /usr/local directory. Depending on the machine, this may require root privileges. Copy the downloaded package file to this directory.
Installation, at least in the UNIX environment, is as simple as unpacking the downloaded package. Execute the following commands to unpack the software and create a symbolic link to the resulting directory:
% cd /usr/local
% tar xzvf apache-tomcat-8.5.X.tar.gz
% ln -s apache-tomcat-8.5.X tomcat
The symbolic link will be useful when upgrading to future versions, minimizing the number path changes to be made in startup scripts. There are a number of configuration options that can be made to a Tomcat deployment but the software will pretty much run out of the box. Extensive documentation with respect to configuration options is available from the Apache Documentation 8 Documentation Index page. That said, this document will cover general and secure configuration for a PDS installation below.
General configuration consists of modifying the port number that the server listens to and enabling access to the Manager interface.
By default, Tomcat comes configured to listen for requests on port 8080. This is actually a very common test port for various web server applications and may conflict with an existing application running in the local environment. To change the port number, execute the following commands to edit the server.xml configuration file (the example uses vi, but any editor will suffice):
% cd /usr/local/tomcat/conf
% vi server.xml
A search for 8080 should discover the following block of XML statements:
<Server port="8005" shutdown="SHUTDOWN">
...
<Service name="Catalina">
...
<Connector port="8080" protocol="HTTP/1.1"
connectionTimeout="20000"
redirectPort="8443" />
...
</Service>
</Server>
In general, ports 1023 and below are commonly reserved by the system and require root user privileges to access. Ports 1024 through 49151 are sporadically used by applications registered with IANA. If the need is for another available port, than ports in the 9000 range are commonly available without conflict in most environments. The following three scenarios will help guide the port selection:
Another common configuration change involves enabling the Manager interface. The Manager interface is not necessary to run Tomcat but it is nice for viewing status and deploying applications. In order to enable the interface, an account must be specified in the Tomcat users configuration file with the appropriate role. Execute the following commands to edit the tomcat-users.xml configuration file:
% cd /usr/local/tomcat/conf
% vi tomcat-users.xml
Add the two XML statements listed below within the <tomcat-users> block.
<tomcat-users>
...
<role rolename="manager-gui"/>
<user username="<username>" password="<password>" roles="manager-gui"/>
...
</tomcat-users>
The first statement defines the manager-gui role and the second statement defines a user with that role. Replace the <username> and <password> in the second statement with desired values for the local environment. This document discusses using the Manager interface in the Deploy Application section below.
The Tomcat application server allows environment-specific variables to be set and utilized by the server. This is accomplished by creating a file named setenv.sh in the /usr/local/tomcat/bin directory. This file will be sourced by the startup script specified in the Launch Tomcat section below. To adjust the memory settings for Tomcat, the contents of the file should look something like the following:
#!/bin/sh
CATALINA_OPTS="-Xms512m -Xmx2048m"
Note: For Red Hat RPM installations, the environment variables can be specified in the /etc/tomcatX/tomcatX.conf file where X is the major version of Tomcat. Although the environment configuration is not limited to the following variables, these two are the most common:
This environment variable allows the user to pass in application-specific Java properties to the applications that are deployed on the Tomcat server. In the example above, the initial and maximum memory settings for Tomcat are specified. Although exhaustive testing has not been performed, these settings have worked well in a number of environments. The location of the Derby database for the Registry Service may also be specified in this variable with the derby.system.home property. This property is described in more detail in the Installation document for the Registry Service.
In most environments there will be one Java installation and this variable should reference the root directory of that installation (i.e., JAVA_HOME=/usr/local/java).
In order to address issues that arise from IT Security scans (e.g., Cross-Site Scripting, Blind SQL Injection, etc.), the Filter component was developed to filter parameter values passed into web applications installed under the Tomcat Server. The Installation document for the Filter component provides the details for downloading, installing and configuring the software.
In addition to filtering user input, the Tomcat Server should also set the secure attribute for cookies. To set this attribute, execute the following commands to edit the web.xml configuration file:
% cd /usr/local/tomcat/conf
% vi web.xml
A search for session-config should discover the following XML block statements:
<session-config>
<session-timeout>30</session-timeout>
</session-config>
Replace the above block with the following:
<session-config>
<session-timeout>30</session-timeout>
<cookie-config>
<http-only>true</http-only>
<secure>true</secure>
</cookie-config>
</session-config>
Then restart the Tomcat Server.
As of Build 9a, the Engineering Node is requiring a secure configuration for its Tomcat Server instances (accepting incoming traffic on port 8443 via HTTPS). Details on this configuration will be provided at at later date.
Launching the Tomcat server is relatively straight forward as long as the JAVA_HOME environment variable is set appropriately. Execute the following commands to launch the Tomcat server:
% cd /usr/local/tomcat/bin
% ./startup.sh
If launching the Tomcat server automatically upon system startup is desired, the Tomcat Setup portion of the Tomcat documentation provides details on setting this up. Alternatively, consult your system administrator for standard mechanisms of accomplishing this in the local environment. Once the Tomcat server has been launched by one of the methods above, the server should be accessible via the following URL: http://localhost:8080/ or http://localhost:8443/ (depending on the configuration). This assumes the listening port was not changed during the configuration. Accessing this URL from the desired web browser, should produce the following display:
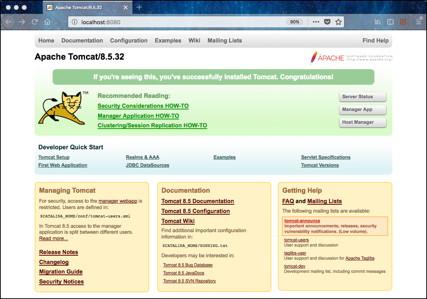
There are a few methods for deploying web applications (e.g., Registry Service, Registry User Interface, etc.) to the Tomcat server and two of them are discussed here. The first is to simply copy the WAR file from the software distribution package into the /usr/local/tomcat/webapps/ directory. The second is to access the Tomcat Manager interface from the Manager App button on the Welcome page displayed in the image above. The user is prompted to enter the username and password that was specified during the configuration. Upon successful authentication and authorization, the following page should be displayed:
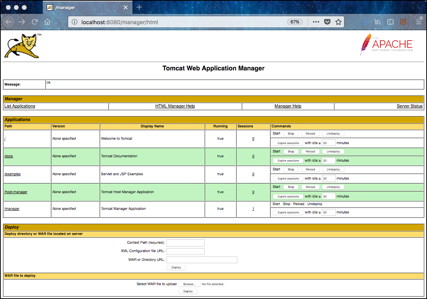
Scrolling down towards the bottom of the page will expose the WAR file to deploy section of the page. From there, choose the WAR file from a local disk and then select the Deploy button to deploy the application to the Tomcat server.
For both methods of deployment, the application will be accessible from the base URL followed by a "/" and then the name of the WAR file minus the extension. So, the Registry Service would be accessible at the following URL: http://localhost:8080/registry/. This assumes the user followed the installation instructions for the Registry Service and renamed the WAR file to registry.war.